Enrolment Link: Credit Risk Management Course
Credit Risk Management is an essential tool to help banks, NBFCs, and fintechs evaluate a borrower’s reliability, minimize defaults, and build resilient portfolios. Additionally, it allows banking institutions to identify risks early, make informed lending decisions, and maintain profits, even during market disruptions, by using data analytics, automation and governance.
What Is Credit Risk Management?
Credit risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risk of financial loss when a borrower fails to meet debt obligations. It’s a cornerstone of modern risk management in banking, ensuring financial institutions lend responsibly while protecting capital.
With increasing economic volatility, digital lending, and tighter regulations, a strong credit risk management framework helps banks and NBFCs minimize non-performing assets (NPAs) and maintain portfolio quality.
What are the 4 Types of Credit Risk?
Understanding the types of credit risk helps institutions design better mitigation strategies:
- Default Risk – Default risk is when borrowers fail to make scheduled payments.
- Concentration Risk – Overexposure to a single borrower, sector, or geography may lead to concentration risk.
- Counterparty / Settlement Risk – It is when one party in a transaction fails to meet obligations.
- Sovereign / Country Risk – This refers to political or regulatory instability impacting repayments.
Why does Credit Risk Management Matters?
In banks, credit risk management is crucial to reduce defaults, increase profits, comply with regulations, and strengthen trust. Here’s a breakdown
- Protects profitability: It helps minimizes losses from loan defaults by timely monitoring
- Ensures compliance: Aligns with Basel norms and RBI guidelines.
- Improves decision-making: Enables data-driven lending and pricing.
- Builds trust: Enhances investor and customer confidence.
- Supports sustainable growth: Balances risk with return for long-term stability.
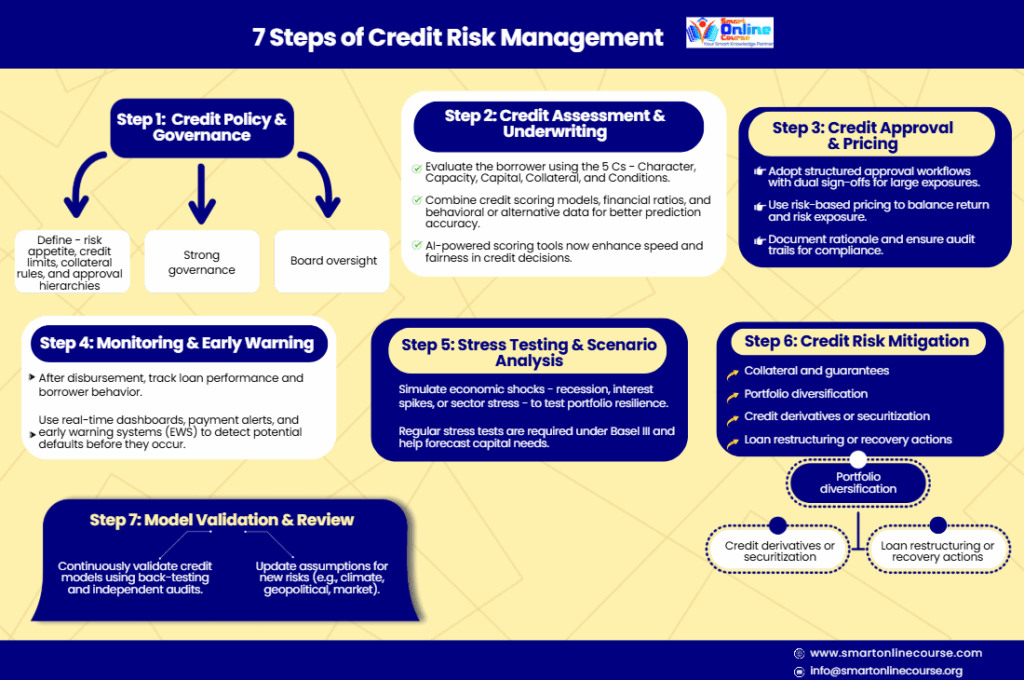
7 Steps of Credit Risk Management Process
A solid credit risk management framework typically follows eight stages:
Credit Policy & Governance
Define risk appetite, credit limits, collateral rules, and approval hierarchies. Strong governance and board oversight ensure consistency and accountability.
Credit Assessment & Underwriting
Evaluate the borrower using the 5 Cs — Character, Capacity, Capital, Collateral, and Conditions.
Combine credit scoring models, financial ratios, and behavioral or alternative data for better prediction accuracy.
AI-powered scoring tools now enhance speed and fairness in credit decisions.
Credit Approval & Pricing
Adopt structured approval workflows with dual sign-offs for large exposures.
Use risk-based pricing to balance return and risk exposure.
Document rationale and ensure audit trails for compliance.
Monitoring & Early Warning
After disbursement, track loan performance and borrower behavior.
Use real-time dashboards, payment alerts, and early warning systems (EWS) to detect potential defaults before they occur.
Stress Testing & Scenario Analysis
Simulate economic shocks — recession, interest spikes, or sector stress — to test portfolio resilience.
Regular stress tests are required under Basel III and help forecast capital needs.
Credit Risk Mitigation
Manage exposure through:
- Collateral and guarantees
- Portfolio diversification
- Credit derivatives or securitization
- Loan restructuring or recovery actions
Model Validation & Review
Continuously validate credit models using back-testing and independent audits.
Update assumptions for new risks (e.g., climate, geopolitical, market).
Challenges in Credit Risk Management
- Data quality issues: Incomplete or inconsistent borrower data.
- Model risk: Outdated models misprice credit exposure.
- Economic uncertainty: Rapid shifts change default probabilities.
- Regulatory changes: Frequent compliance updates increase complexity.
- Concentration risk: Overexposure to a single sector or region.
Best Practices for Effective Credit Risk Management
Automate and Digitize
Adopt AI-driven credit risk platforms to automate data collection, scoring, and monitoring. In banks, automation improves speed, accuracy, and scalability while reducing human bias.
Real-Time Monitoring
Integrate cloud-based tools to track portfolio health and borrower performance. Set EWS triggers for repayment delays or rating downgrades.
Diversify Exposure
Spread lending across industries, geographies, and borrower categories to reduce concentration risk.
Align with Regulations
Comply with Basel III and IFRS 9 standards for capital adequacy and provisioning. Maintain accurate risk-weighted asset (RWA) reporting.
Build a Risk-Aware Culture
Train teams in risk analytics and fraud prevention. Encourage disciplined decision-making and accountability across all lending functions.
Emerging Trends in Credit Risk Management
- AI and Machine Learning: Predictive modeling for early delinquency detection.
- Alternative Data: Inclusion of transaction and behavioral data for thin-file borrowers.
- ESG Credit Risk: Integrating environmental and governance risks into credit ratings.
- Blockchain Data Sharing: Secure, tamper-proof credit histories.
- Cloud-Native Platforms: Unified, real-time risk dashboards.
An effective credit risk management framework protects financial institutions from losses while enabling growth and boosting portfolio. It combines robust policy frameworks, AI-enabled analytics, and sound governance to make informed decisions.
Check out more Risk Management Courses at Smart Online Course or RMAI Courses.
Found this blog insightful? Here’s our 20-hour Credit Risk Management course for in-depth understanding. You will get a credit risk management certification from this online course.
Explore Credit Risk Management Course Now!


